Slow Internet, is perhaps the most pestering issue faced by a modern virtual society, especially for those of us who have made it their abode. It is far peskier than having no Internet at all, since in the latter case, the person can at least look at other means of entertainment. Today, we are going to look at the reasons why your internet speeds might not be up to the mark.

If you hate this screen more than anything, and it happens to you often, proceed on to know about possible reasons why the shadow of slow speed has been haunting your life.

Before we begin, let’s try and understand exactly how the Internet gets to you. Any website that you access gets to you through a series of complex mechanisms either working side by side or in quick succession of one another. You send a request package that goes through multiple connections and routing points till it gets to the host, which in return sends back data, which again gets back to you along the same path.
Remember the “Relay Races” from the good old days? Yes, the ones where a dude had to run a certain length of track with the mantle (baton), pass it on to his teammate,
who would then run another length of the track before passing it on to the guy waiting next in line, and this would go on till the entire track was covered by a particular team deemed as winners.
What did it take to win races like this?
Obviously, it didn’t matter which team had the fastest runner, since all he could cover was but a certain length of the track, what mattered was which team had above average runners with a high degree of coordination.
Likewise in case of your Internet too, a single slow player can cause the entire team to suffer; your entire apparatus to run slowly.
Zeroing in on the problem
To start off, you should run a speed test to determine whether or not the speed is consistent with what your ISP claims. In case it is not, immediately call your ISP to make an inquiry.
Next, try checking connectivity with multiple websites and observe how they perform. In case most websites run fine, the problem may be at the server’s end. We are discussing these issues since there is not much we as users can do about them, these are your teammates in the relay, whose performance, your practice cannot help.
Major Issues:
1. Viruses & Malware:
Viruses generally infect stored data, but they can cause your system to slow down on the whole. A virus can overload your browser’s cache and cause it to respond slowly, sending across an impression of the internet having slowed down.
What you should actually be concerned about, are internet worms.
They are malicious software programs that can spread from one device to another over the network.
Even if one of your computers becomes infected by an internet worm, it can spontaneously generate network traffic without your knowledge, and cause your internet connection to appear slow.
2. Bandwidth Hogging Background Applications:
Background applications are software applications that run in the background, hidden behind other applications or minimized to the system tray. They quietly consume network resources, unless you decide to run the task manager and close them manually.

Like Google Drive, Dropbox, iCloud, Google Cloud, Games and programs that work with videos/streaming require significant bandwidth thus limiting bandwidth for apps you are running.
3. Problems with LAN Connectors/Access Points
If your connection is a wired setup,
- If you are using home built cable, throw this away and buy a cable.
- Check for the length. This is probably not your problem, because Cat5/6 cable all have the same length specifications for 1Gbps Ethernet; 100 meters or about 320 feet. If you are over this length, get a shorter cable.
- Third, and a very common problem, is interference from an external source such as a florescent light, microwave oven, or speaker. Move your cables away from these sources of interference by a couple of feet.
- Verify that the devices plugged into your router or switch are set to the correct duplex and speed. If speed and duplex cannot be set manually, your device should be set to auto-negotiate mode, failure to do this will result in a duplex mismatch.
If your connection is wireless,
However, you need to take a separate set of measures. For starters, make sure your WiFi router is not in a bad spot. A bad spot is a place surrounded by many signal absorbing materials.
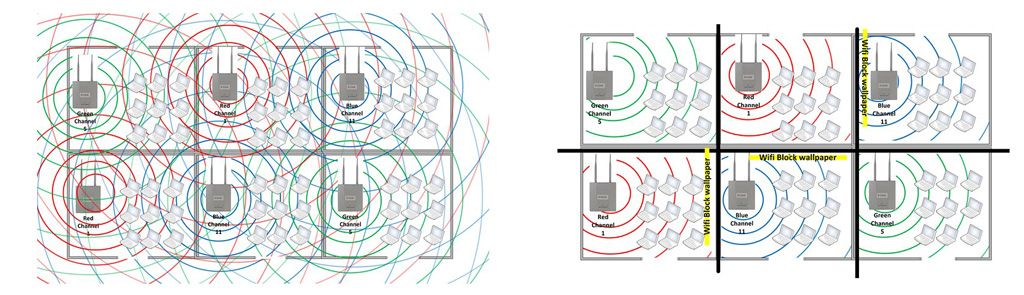
The airwaves could be congested with too many devices nearby, especially if you’re using a 2.4 GHz router, which can support a lot more devices. This is a particularly common problem in denser urban areas.
Rebooting your modem or router can provide temporary relief from this problem, as it resets all connections and the devices hence disconnected require some time to get their background processes back on, but if this is a regular occurrence, you need to try signal boosting and relocation.
4. Saturation of Connection
As a rule of thumb, the more is the number of devices around you, the more saturated the connection is going to be.
Imagine your devices are tug of war players with your router in the middle.

For example, if multiple activities like downloads, streaming, gaming, etc. are being carried out simultaneously, the result is going to be an immense cumulative load on the system.
If this is a particularly frequent problem, you should consider upgrading your internet package. However, some routers also have a Quality of Service (QoS) feature, which can automatically manage and assign the required bandwidth to different devices and services.
5. DNS Issues
DNS Server is the ticket window guy who hands you the ticket you need to travel. In our case, as and when you need to connect to some website, your machine contacts its DNS server and asks for its ticket to travel to Internet.
“What IP address is associated with google.com?” It gets an address in answer and connects to that IP address.
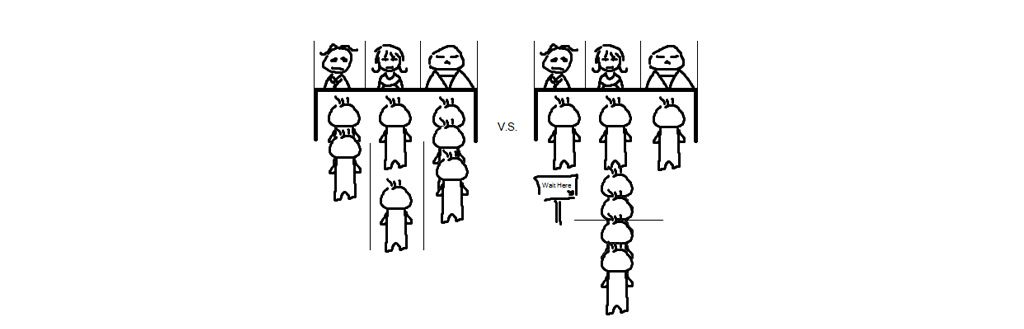
Typically, your DNS servers are provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). But, a proportion of traffic higher than usual, can cause them to overload. In such a scenario, you have a chance at better speed by switching to another set of DNS servers.
Its like, which queue shall you choose in the interests of saving time?
Conclusion
So to sum all that up, we can safely conclude that the Internet as well as the problems that go with it are not dependent on one single factor but a multitude of them, and a disruption in any of these factors causes the entire system to slow down. Next, we looked at some of these factors which could be compromising your overall online experience. It is a common observation that in 86% of the cases where there is not an ISP outage, it is one of these factors that is at play.
Anything that crosses your mind about a point we missed, feel free to comment below and don't forget to subscribe to our email newsletter for more cool tech stuff.
Cheers and Happy Reading!


Comments
Become a BhaiFi® | Blog & Stories member below to join the conversation (it's free!). As a member, you will also receive new posts by email (you can unsubscribe at any time).